What is diabetes | Causes | Signs and Symptoms | Classification | Risk factor | Diagnosis | Treatment | Complications | Prevention | Diet | Exercise | Summary
What is Diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic medical condition characterized by high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. The body uses glucose as its main source of energy. But it requires a hormone called insulin to help transport the glucose from the bloodstream into the cells.
In individuals with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin (type 1 diabetes). Or the cells do not respond properly to insulin (type 2 diabetes), leading to high blood sugar levels.
Gestational diabetes is a temporary condition that occurs during pregnancy.
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputations. However, with proper management and treatment, individuals with diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
Causes of Diabetes

The exact causes of diabetes vary depending on the type of Diabetes mellitus.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder. Which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The exact cause of this is not fully understood. But it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and weight. Insulin resistance, in which the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin. Is a major factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. Being overweight or obese and having a sedentary lifestyle can also increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is caused by hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy. These changes make it more difficult for the body to use insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Other possible causes of diabetes include certain medications, diseases of the pancreas, and viral infections.
Overall, the exact causes of diabetes are not fully understood. And research is ongoing to determine the underlying mechanisms of the disease.
Signs and Symptom of Diabetes mellitus
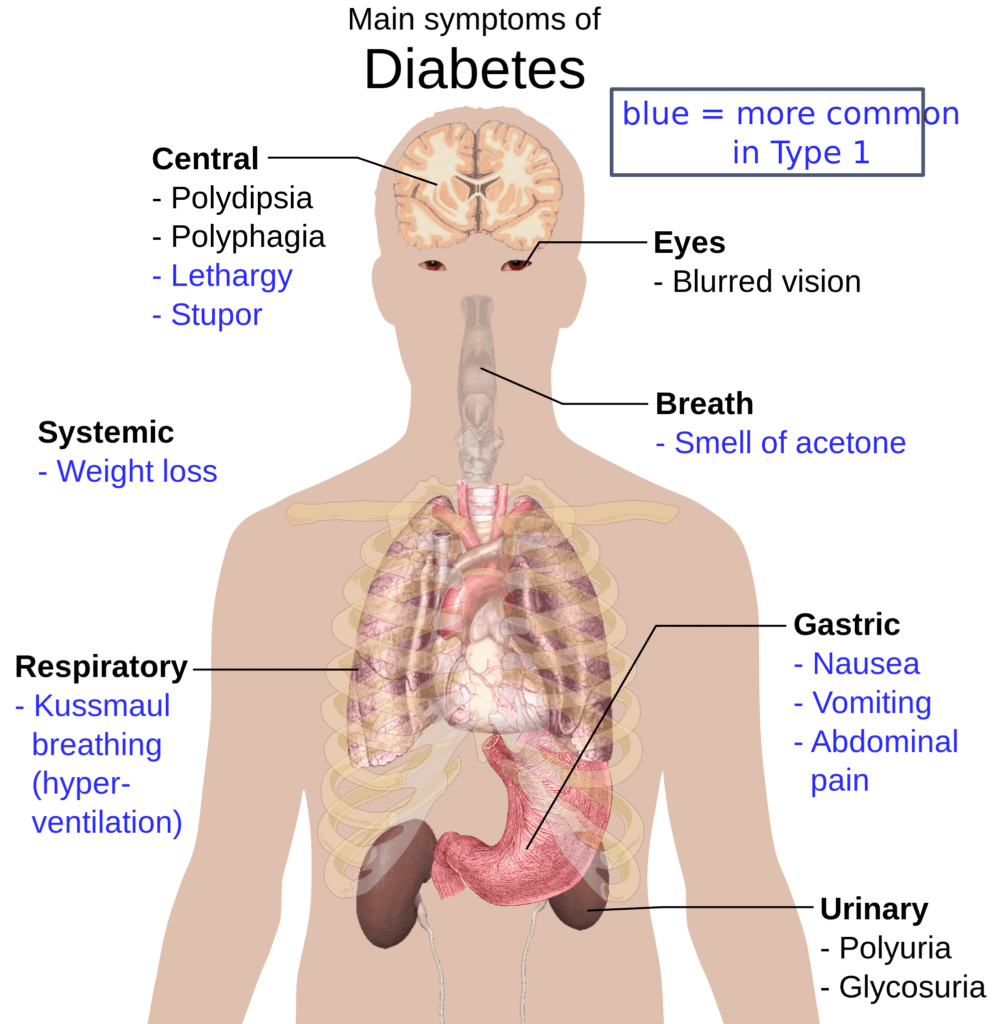
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that results in the destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It typically develops in childhood or adolescence, but can occur at any age. Signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes can appear suddenly and can be severe. They include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination: The body tries to flush out excess sugar by producing more urine. Which can lead to dehydration and increased thirst.
- Hunger: Despite eating more, people with type 1 diabetes may lose weight. Because the body is not able to use glucose for energy.
- Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can make an individual feel tired and weak.
- Blurred vision: Diabetes can cause changes in the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blurry vision.
- Slow-healing wounds: Diabetes can affect the body’s ability to heal, leading to slow-healing cuts, sores, or wounds.
- Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves. Leading to tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
- Unusual weight loss: Some people with diabetes may lose weight without trying. Due to the body’s inability to use sugar for energy.
- Yeast infection: Women with diabetes are more susceptible to yeast infection.
- Ketoacidosis: type 1 diabetics are susceptible to a serious complication called ketoacidosis. Which is a build-up of acids in the blood due to the body’s inability to produce insulin. Symptoms of ketoacidosis include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and difficulty breathing.
If you suspect you or someone you know may have type 1 diabetes, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that occurs when the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin. Or when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to keep blood sugar levels under control. It is typically diagnosed in adults. But is becoming increasingly common in children and adolescents due to the rise in obesity. The signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes may develop slowly and can be mild or absent in some cases. They include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination: The body tries to flush out excess sugar by producing more urine. Which can lead to dehydration and increased thirst.
- Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can make an individual feel tired and weak.
- Blurred vision: Diabetes can cause changes in the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blurry vision.
- Slow-healing wounds: Diabetes can affect the body’s ability to heal, leading to slow-healing cuts, sores, or wounds.
- Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves. Leading to tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
- Unusual weight loss: Some people with diabetes may lose weight without trying. Due to the body’s inability to use sugar for energy.
- Yeast infection: Women with diabetes are more susceptible to yeast infection.
- Darkening of the skin: Type 2 diabetes can cause dark patches on the skin, usually in the armpits and neck.
- Dry mouth and itchy skin: Due to the high sugar in the blood, dry mouth. And itchy skin are common symptoms.
It’s important to note that many people with type 2 diabetes may not have any symptoms at all. Or the symptoms may be so mild that they go unnoticed. Therefore, it’s important to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to screen for diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes mellitus
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy and typically goes away after the baby is born. It occurs when the body is not able to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demand during pregnancy. The signs and symptoms of gestational diabetes may be mild or absent, but can include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination: The body tries to flush out excess sugar by producing more urine. Which can lead to dehydration and increased thirst.
- Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can make an individual feel tired and weak.
- Blurred vision: Diabetes can cause changes in the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blurry vision.
- Slow-healing wounds: Diabetes can affect the body’s ability to heal, leading to slow-healing cuts, sores, or wounds.
- Yeast infection: Women with diabetes are more susceptible to yeast infection.
- Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves. Leading to tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
- Unusual weight loss: Some people with diabetes may lose weight without trying. Due to the body’s inability to use sugar for energy.
- Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can make an individual feel tired and weak.
- Urinary tract infection: Due to the high sugar in the blood, urinary tract infection is common in gestational diabetes
It’s important to note that many women with gestational diabetes may not have any symptoms at all. Or the symptoms may be so mild that they go unnoticed. Therefore, it’s important to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider during pregnancy to screen for gestational diabetes.
Classification of diabetes mellitus
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. The classification of diabetes is based on the causes of the disease and how it affects the body. The main types of diabetes are:
- Type 1 diabetes: Also known as insulin-dependent diabetes or juvenile diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks. And destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body is not able to produce enough insulin to control blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 diabetes: Also known as non-insulin dependent diabetes or adult-onset diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and weight. It occurs when the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin. Or when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to keep blood sugar levels under control.
- Gestational diabetes: This type of diabetes develops during pregnancy and typically goes away after the baby is born. It occurs when the body is not able to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demand during pregnancy.
- Other types of diabetes: There are other types of diabetes. Such as maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) and secondary diabetes. Which is caused by other diseases or certain medications.
It’s important to note that the classification of diabetes is not always clear-cut. And some individuals may have characteristics of more than one type of diabetes. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the type of diabetes you have.
Risk factor of diabetes
There are several risk factors that can increase an individual’s likelihood of developing diabetes. These include:
- Family history: Having a parent or sibling with diabetes increases the risk of developing the disease.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. As excess body fat can make it more difficult for the body to use insulin.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Age: The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases as people age, especially after the age of 45.
- High blood pressure: Hypertension is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
- Abnormal cholesterol and triglyceride levels: High levels of cholesterol or triglycerides in the blood. Can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS are at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes.
- Previous gestational diabetes: Women who have had gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Prediabetes: Having high blood sugar but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. Also puts an individual at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
It’s important to note that not everyone with these risk factors will develop diabetes. And some people with diabetes may not have any known risk factors.
Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
Diabetes is usually diagnosed through a combination of blood tests. The most common tests used to diagnose diabetes are:
- Fasting blood glucose test: This test measures the level of glucose in the blood. After an individual has gone without food for at least 8 hours. A fasting blood glucose level of 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate occasions indicates diabetes.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: This test measures the body’s ability to handle glucose. The individual will fast overnight and then have their blood glucose level measured. They will then drink a sugary drink, and their blood glucose level will be measured again after 2 hours. A blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or higher on this test indicates diabetes.
- Random blood glucose test: This test measures the level of glucose in the blood at any time of the day. Regardless of when the individual last ate. A random blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or higher, along with symptoms of diabetes, indicates diabetes.
- HbA1C: This test measures the average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months. A HbA1C level of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes.
It’s important to note that if an individual is suspected of having diabetes. A healthcare professional will typically repeat the test on a different day to confirm the diagnosis.
For gestational diabetes, it’s usually diagnosed between 24-28 weeks of pregnancy through a glucose tolerance test.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns about diabetes. They will be able to guide you with the appropriate test.
Treatment of diabetes mellitus

Home treatment
Home treatment for diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes. And self-management strategies to help control blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Some home treatment options for diabetes include:
- Monitoring blood sugar levels: Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels at home. Can help individuals with diabetes to better understand how their diet, exercise, and medications affect their blood sugar levels.
- Eating a healthy diet: Eating a diet that is high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. And low in saturated and trans fats can help control blood sugar levels and promote overall health.
- Getting regular exercise: Regular physical activity can help to control blood sugar levels, promote overall health. And reduce the risk of complications.
- Taking medications as prescribed: Taking diabetes medications as directed by a healthcare professional can help to control blood sugar levels.
- Managing stress: Stress can affect blood sugar levels. So it’s important to find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, and meditation.
- Regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help to detect and prevent complications of diabetes.
- Proper foot care: People with diabetes are at risk of developing foot problems. So it’s important to keep feet clean, dry. And well-cared for, checking them daily for cuts, blisters, or other signs of injury.
- Smoking cessation: Smoking is a risk factor for diabetes-related complications. So it’s important for individuals with diabetes to quit smoking if they smoke.
It’s important to work closely with a healthcare professional to create a home treatment plan that is right for you. They can also help you to monitor your progress and make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
Medications treatment
Medications are a common treatment option for Diabetes mellitus. And the type of medication prescribed will depend on the type of Diabetes mellitus and the individual’s overall health. Some of the most common medications used to treat diabetes include:
- Insulin: Insulin is a hormone that helps to control blood sugar levels. Individuals with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2 diabetes require insulin therapy to manage their diabetes. Insulin can be administered via injections or an insulin pump.
- Oral medications: Metformin is the most commonly prescribed oral medication for type 2 diabetes. It helps to lower blood sugar levels by decreasing glucose production in the liver. And increasing the body’s sensitivity to insulin. Other oral medications that can be prescribed include sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors.
- Incretin-based therapy: Incretin-based therapy is a group of medication that mimic the actions of incretin hormones. Which are naturally occurring hormones that help to regulate glucose levels after eating. These medications include GLP-1 receptor agonists and DPP-4 inhibitors.
- Combination therapy: In some cases, a combination of medications may be prescribed to better control blood sugar levels.
It’s important to note that medication for diabetes should be taken only under the guidance of a healthcare professional. And the treatment plan may change over time as the patient’s needs change. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are important to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and make adjustments as needed.
Complications of diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic medical condition that can lead to a number of serious complications if not properly managed. Some of the most common complications of diabetes include:
- Cardiovascular disease: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure.
- Kidney disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney disease and eventually kidney failure.
- Nerve damage: Diabetes can cause damage to the nerves, known as diabetic neuropathy. Which can lead to numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands, feet, and other parts of the body.
- Eye damage: Diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to a range of eye problems. Including diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma.
- Foot problems: Diabetes can cause damage to the nerves and blood vessels in the feet. Making them more susceptible to infection and injury.
- Skin problems: Diabetes can cause a range of skin problems, including dry and itchy skin. And a higher risk of skin infections.
- Dental problems: Diabetes can make it more difficult for the body to fight infection. Including infections in the mouth, leading to gum disease and other dental problems.
- Sexual dysfunction: Diabetes can cause sexual dysfunction in both men and women. Including impotence in men and vaginal dryness in women.
- Pregnancy complications: Women with gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing high blood pressure, pre-eclampsia. And having a large baby.
It’s important to work closely with a healthcare professional to manage diabetes and prevent complications. Regular check-ups and screenings can help to detect and prevent complications early on.
Prevention of Diabetes mellitus
There are several steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing diabetes. Some preventative measures include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. Losing weight through a combination of diet and exercise can help to reduce the risk of diabetes.
- Eating a healthy diet: Eating a diet that is high in fruits, vegetables and whole grains and low in saturated. And trans fats can help to reduce the risk of diabetes.
- Getting regular physical activity: Regular physical activity can help to control blood sugar levels. And promote overall health, reducing the risk of diabetes.
- Not smoking: Smoking is a risk factor for diabetes-related complications. So it’s important for individuals to quit smoking if they smoke.
- Managing stress: Stress can affect blood sugar levels, so it’s important to find healthy ways to manage stress. Such as exercise, yoga, and meditation.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels: Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels at home. Can help individuals with diabetes to better understand how their diet, exercise, and medications affect their blood sugar levels.
- Regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help to detect and prevent diabetes and related complications.
- Breastfeeding: Women who breastfeed their babies have a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
It’s important to note that not everyone can prevent diabetes. But by making lifestyle changes and working with a healthcare professional. Individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing the disease.
Learn more about diseases
Diet for diabetes disease

- A healthy diet is an important part of managing diabetes and preventing complications. The goal of a diabetes diet is to keep blood sugar levels in a healthy range. While providing the body with the nutrients it needs to stay healthy. Some general guidelines for a diabetes diet include:
- Eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods: Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins. And healthy fats should make up the majority of a diabetes diet.
- Limiting processed foods and added sugars. Processed foods and foods high in added sugars can cause blood sugar levels to spike. So it’s best to limit these foods as much as possible.
- Managing portion sizes: Eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day can help to keep blood sugar levels stable.
- Monitoring carbohydrate intake: Carbohydrates raise blood sugar levels. So it’s important to monitor carbohydrate intake and choose carbs that are high in fiber and nutrients. Such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Being mindful of fats: Eating too much saturated and trans fats can increase the risk of heart disease. Which is a common complication of diabetes. It is important to choose healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
- Planning meals: Planning meals in advance can help to ensure that. The meals are balanced and consistent with a diabetes diet.
It’s important to work with a healthcare professional and a registered dietitian to create a diabetes diet. That is tailored to your specific needs and goals. They can also help you to monitor your progress and make adjustments to your diet as needed.
Exercise for Diabetes mellitus

Regular physical activity is an important part of managing diabetes and preventing complications. Exercise can help to improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and promote overall health. Some general guidelines for exercise for individuals with diabetes include:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. This can include activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing.
- Incorporate strength training exercises: Strength training exercises such as weightlifting, resistance bands, or bodyweight. Exercises can help to build muscle mass, which can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Incorporate flexibility and balance exercises: Exercises that improve flexibility and balance. Such as yoga or tai chi, can help to prevent falls and improve mobility.
- Monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise: Blood sugar levels can drop during exercise. Especially if an individual has taken insulin or certain diabetes medications. So it’s important to monitor blood sugar levels and make adjustments as needed.
- Wear appropriate shoes and socks: Wearing comfortable and well-fitting shoes and socks. Can help to prevent foot injuries and other complications.
- Exercise with a buddy or in a group: Exercising with a buddy or in a group can help to make exercise more enjoyable. And provide motivation to stick with it.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting an exercise program. And to make adjustments to the program as needed. They can help you to create a personalized exercise plan that will work best for you.
Summary of Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic medical condition characterized by high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. It is caused by a lack of insulin production or by the body’s inability to use insulin effectively.
There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2 and Gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks. And destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and weight. It occurs when the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin. Or when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to keep blood sugar levels under control.
Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy and typically goes away after the baby is born.
The main risk factors for diabetes include family history, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, age, high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol. And triglyceride levels, polycystic ovary syndrome and previous gestational diabetes.
The main goals of diabetes treatment are to keep blood sugar levels under control, prevent complications, and improve overall health. This can be achieved through a combination of medications, diet and exercise, blood sugar monitoring, education, and support.
It’s important to work closely with a healthcare professional to manage diabetes and prevent complications. Regular check-ups and screenings can help to detect and prevent complications early on.
learn more about this disease
Additional resources for diabetes mellitus information
- American Diabetes Association (ADA) – This organization provides a wide range of resources for people with diabetes, including information on diabetes management, research, and advocacy.
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF) – This global organization offers information on diabetes statistics, guidelines, and advocacy efforts around the world.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) – This organization, part of the National Institutes of Health, provides research-based information on diabetes and other related conditions.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC provides statistics, resources, and guidelines for diabetes prevention and management.
- Mayo Clinic – The Mayo Clinic is a reputable healthcare provider and research institute that offers a wide range of diabetes information and resources on their website.
- Diabetes.co.uk – It is an online community for people with diabetes, providing information, support and resources to help people manage their condition.
- Diabetes Australia – It is the national body for diabetes in Australia, providing information, support and resources to help people manage their condition.
- Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (JDRF) – This organization focuses on type 1 diabetes research and provides information and resources for people affected by this type of diabetes.
These resources provide a wealth of information on diabetes, from basic information on the condition to detailed information on management, treatment, and research.






Hello! I just would like to give a huge thumbs up for the great info you have here on this post. I will be coming back to your blog for more soon.
he blog was how do i say it… relevant, finally something that helped me. Thanks
Some genuinely nice stuff on this web site, I love it.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Hey! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting fed up of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform. I would be fantastic if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I’ll right away clutch your rss feed as I can not find your email subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please permit me recognize so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
This blog is definitely rather handy since I’m at the moment creating an internet floral website – although I am only starting out therefore it’s really fairly small, nothing like this site. Can link to a few of the posts here as they are quite. Thanks much. Zoey Olsen
You write with such passion and clarity, it’s like listening to a love song for the mind.
naturally like your web site but you have to check the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I in finding it very bothersome to tell the truth however I?¦ll certainly come again again.
The words are like brush strokes on a canvas, painting ideas in my mind.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
A big thank you for your blog article.Thanks Again. Want more.
Perfectly indited subject material, Really enjoyed studying.
Wonderful blog! I found it while searching on Yahoo News. Do you have any suggestions on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Cheers
Thanks , I’ve just been looking for info about this topic for ages and yours is the greatest I’ve discovered so far. But, what about the conclusion? Are you sure about the source?
The Writing has become a go-to resource for me. The effort you put into The posts is truly appreciated.
Unique viewpoints, because who needs echo chambers?
I appreciate the unique viewpoints you bring to The writing. Very insightful!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Hey There. I found your weblog using msn. That is an extremely neatly written article. I will make sure to bookmark it and come back to read extra of your helpful information. Thanks for the post. I’ll definitely return.
Thanks for another informative blog. The place else may just I get that type of info written in such an ideal method? I’ve a undertaking that I’m just now running on, and I’ve been at the glance out for such info.
Lovely just what I was searching for.Thanks to the author for taking his clock time on this one.
Good day very cool website!! Guy .. Excellent .. Amazing .. I will bookmark your blog and take the feeds also…I’m happy to search out so many helpful info here in the post, we need work out extra strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .