INDICATION
Abemaciclib, Indicated in combination with fulvestrant for the treatment of women with hormone receptor (HR)-positive. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression following endocrine therapy.
Abemaciclib Indicated as mono-therapy for the treatment of adult patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced. Or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression following endocrine therapy and prior chemotherapy in the metastatic setting.
Doses
Adult dosage
Tablet
50mg
100mg
150mg200mg
Early Breast Cancer
Adult dosage
150 mg orally twice a day PLUS tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor (see Prescribing Information)
Continue for 2 years, or until disease recurrence or unacceptable toxicity
Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
Adult dosage
Mono-therapy
200 mg orally twice a day
Continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity
Combination therapy with an aromatase inhibitor
150 mg orally twice a day PLUS an aromatase inhibitor (see Prescribing Information)
Combination therapy with fulvestrant
150 mg orally twice a day PLUS
Fulvestrant 500 mg Intramuscular on Days 1, 15, and 29, and then once monthly thereafter
Dosage Modifications
Adult dosage
Dosage modifications for adverse effects
Combined with fulvestrant, tamoxifen, or an aromatase inhibitor
Starting dose: 150 mg twice a day
First dose reduction: 100 mg twice a day
Second dose reduction: 50 mg twice a day
Discontinue if unable to tolerate 50 mg twice a day
Mono-therapy
Starting dose: 200 mg twice a day
First dose reduction: 150 mg twice a day
Second dose reduction: 100 mg twice a day
Third dose reduction: 50 mg twice a day
Discontinue if unable to tolerate 50 mg twice a day
Administration
Abemaciclib, May be taken with or without food.
Instruct patient to take dose at approximately the same time each day.
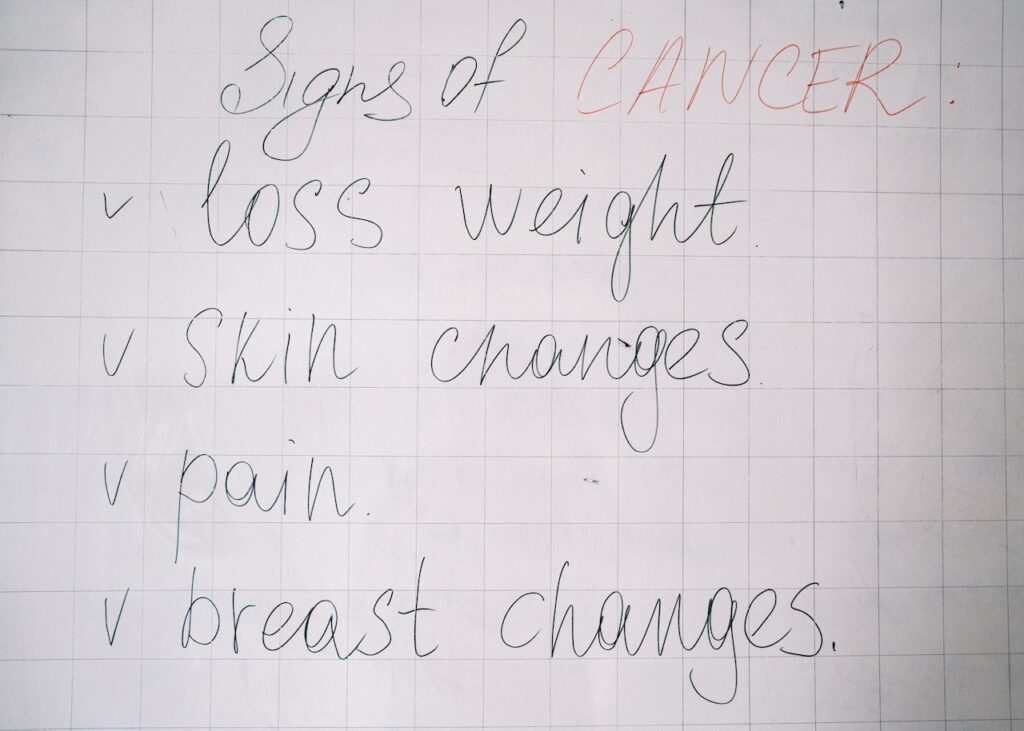
Contraindications
Abemaciclib, Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredient of this product.
Side effects:
Common side effects of Abemaciclib include:
Diarrhea, low white blood cell count (neutropenia, leukopenia), nausea, abdominal pain. Infections, fatigue, anemia, decreased appetite, vomiting, headache, low blood platelet count (thrombocytopenia), sores.
And inflammation inside the mouth, swelling of extremities, fever, cough, hair loss, itching, rash. Changes in taste, dizziness, alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, and weight loss.
Serious side effects of Abemaciclib include:
- Severe or ongoing diarrhea; pain or burning while urinating;
- liver problems–right-sided upper stomach pain, loss of appetite, easy bruising or bleeding, feeling very tired;
- low blood cell counts–fever, chills, tiredness, mouth sores, skin sores, easy bruising, unusual bleeding, pale skin, cold hands and feet, feeling light-headed or shortness of breath;
- signs of inflammation in the lungs–new or worsening cough, painful or difficult breathing, wheezing, feeling short of breath even while resting; or
- signs of a blood clot–pain or swelling in an arm or leg, chest pain, fast heartbeats, feeling short of breath.
Rare side effects of Abemaciclib include:
None
This is not a complete list of side effects. And other serious side effects or health problems that may occur as a result of the use of this drug. Call your doctor for medical advice about serious side effects or adverse reactions. You may report side effects or health problems to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Precaution & Warnings
- May cause fetal harm; advise women of reproductive potential to use effective contraception (see Pregnancy)
- Interstitial lung disease
- Severe, life-threatening, or fatal ILD and/or pneumonitis can occur; additionally cases of ILD/pneumonitis have been observed in the post-marketing setting, with fatalities reported; monitor for pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis which may include hypoxia, cough, and dyspnea
- Dose interruption or dose reduction is recommended for patients who develop persistent or recurrent Grade 2 ILD/pneumonitis; permanently discontinue therapy in all patients with Grade 3 or 4 ILD or pneumonitis
Venous thromboembolism
- In any case clinical trials, venous thromboembolic events (VTE) were reported in patients treated with abemaciclib plus an aromatase inhibitor (5%) and in patients treated with abemaciclib plus fulvestrant (5%)
- VTE (.g, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, pelvic venous thrombosis, subclavian and axillary vein thrombosis, inferior vena cava thrombosis) reported in patients receiving abemaciclib and fulvestrant
- Therapy has not been studied in patients with early breast cancer with a history of venous thromboembolism
- Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism and treat them as medically appropriate
- Dose interruption is recommended for early breast cancer patients with any grade venous thromboembolic event and advanced or metastatic breast cancer patients with a Grade 3 or 4 venous thromboembolic event
- Hepatotoxicity
- Increased transaminases were observed in clinical trials
- In patients who had a grade above 3 ALT elevation, the median time-to-onset was 57 days; whereas, a grade below 3 was 14 days
- In patients who had a grade above 3 AST elevation, the median time-to-onset was 185 days; whereas, a grade below 3 was 13 days
- Monitor liver function tests (LFTs) before the start of therapy, every 2 weeks for the first 2 months, monthly for the next 2 months, and as clinically indicated; dose interruption, dose reduction, dose discontinuation, or delay in starting treatment cycles is recommended for patients who develop persistent or recurrent Grade 2, or Grade 3 or 4, hepatic transaminase elevation
Neutropenia
- Neutropenia was observed in clinical trials; in patients with a grade above 3 neutropenia, the median time time-to-onset was 29 days and the median duration was 15 days
- Febrile neutropenia was reported in below 1% of patients exposed to abemaciclib in the MONARCH studies; 2 deaths due to neutropenic sepsis were observed in MONARCH 2
- Monitor complete blood counts before starting therapy, every 2 weeks for the first 2 months, monthly for the next 2 months, and as clinically indicated; dose interruption, dose reduction, or delay in starting treatment cycles is recommended for patients who develop Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia; inform patients to promptly report any episodes of fever to their healthcare provider
Diarrhea
- Diarrhea incidence was reported to be greatest during the first month of dosing
- Diarrhea occurred in 81% of patients receiving abemaciclib plus an aromatase inhibitor in MONARCH 3, 86% of patients receiving abemaciclib plus fulvestrant in MONARCH 2, and 90% of patients receiving abemaciclib alone in MONARCH 1
- Episodes of diarrhea have been associated with dehydration and infection; diarrhea incidence was greatest during the first month of dosing
- Instruct patients that at the first sign of loose stools, they should start antidiarrheal therapy such as loperamide, increase oral fluids, and notify the healthcare provider for further instructions and appropriate follow up; for Grade 3 or 4 diarrhea, or diarrhea that requires hospitalization, discontinue treatment until toxicity resolves to below Grade 1, and then resume treatment at next lower dose
Drug interaction overview
- Abemaciclib is metabolized to several metabolites primarily by CYP3A4
- Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increased the exposure of abemaciclib plus its active metabolites to a clinically meaningful extent and may lead to increased toxicity
- Ketoconazole: Avoid coadministration
- Other strong CYP3A inhibitors: Decrease recommended starting dose (see Dosage Modifications)
- Strong CYP3A inducers: Avoid coadministration
Pregnancy and Lactation
- There are no available human data are informing the drug-associated risk
- Based on findings from animal studies and the mechanism of action, can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman; advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus
- In animal data, administration of abemaciclib during organogenesis was teratogenic and caused decreased fetal weight at maternal exposures that were similar to human clinical exposure based on AUC at the maximum recommended human dose
- Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential before initiating treatment
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose
- Based on findings in animals, abemaciclib may impair fertility in males of reproductive potential
Lactation
- Unknown if distributed in human breast milk
- Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants, advise lactating women not to breastfeed while taking abemaciclib and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose
Therapeutic class
Antineoplastics CDK Inhibitors.
Drug mode of action
Regulation of cell cycle is crucial in maintaining proper cell growth. Dysregulated cell cycle signalling pathway is a key component in inducing hyperproliferation of cells and also tumor formation in various cancers.
G1 to S phase cell cycle progression, or transition through the G1 restriction point (R), is promoted by the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein (Rb)-mediated pathway.
as well as activation of Rb-mediated pathway requires the interaction of Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) 4 and 6 with D-type cyclins. Which drives the formation of active CDK4/CDK6 and subsequent phosphorylation of Rb 1,2.
RB
Rb is a tumor suppressant protein that inhibits proliferation through binding to. And suppressing the activity of the E2F family of transcription factors 1.
However, phosphorylation of Rb relieves suppression of E2F to allow expression of genes. Required for passage through the restriction point 1.
This leads to increased expression of downstream signalling molecules. Also activity of protein kinases that promote the cell cycle progression and initiation of DNA replication.
Phosphorylation of Rb and other proteins by CDK4/6 additionally leads to transcription of genes. Involved in cell cycle-independent activities including signal transduction, DNA repair transcriptional control, and mRNA processing 1.
Inhibits
Abemaciclib selectively inhibits CDK4 and CDK6 with low nanomolar potency. Inhibits Rb phosphorylation resulting in a G1 arrest and inhibition of proliferation. And its activity is specific for Rb-proficient cells 1. Unlike other CDK inhibitors such as Palbociclib and Ribociclib, abemaciclib exhibits greater selectivity for CDK4 compared to CDK6 2.
Drug Interaction
If your medical doctor is using this medicine to treat your pain. Your doctor or pharmacist may already be aware of any possible drug interactions and may be monitoring you for them. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicine before checking with your doctor, health care provider, or pharmacist first.
- Abemaciclib has severe interactions with no other drugs
- Abemaciclib has serious interactions with at least 42 other drugs.
- Abemaciclib has moderate interactions with at least 44 other drugs.
- Abemaciclib has minor interactions with no other drugs
This information does not contain all possible interactions or adverse effects.
Therefore, before using this product, tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the products you use. Keep a list of all your medications with you and share this information with your doctor and pharmacist. Check with your health care professional or doctor for additional medical advice, or if you have health questions or concerns.
More about Generic medicines click below link





I think other website proprietors should take this site as an model, very clean and wonderful user friendly style and design, as well as the content. You are an expert in this topic!
hi!,I like your writing so much! share we communicate more about your article on AOL? I need a specialist on this area to solve my problem. Maybe that’s you! Looking forward to see you.
F*ckin’ tremendous things here. I am very satisfied to look your article. Thank you so much and i am taking a look ahead to contact you. Will you please drop me a mail?
Oh my goodness! a tremendous article dude. Thank you Nevertheless I am experiencing difficulty with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anybody getting identical rss downside? Anybody who knows kindly respond. Thnkx
It’s a pity you don’t have a donate button! I’d definitely donate to this brilliant blog! I suppose for now i’ll settle for book-marking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to fresh updates and will share this blog with my Facebook group. Chat soon!
constantly i used to read smaller content that also clear their motive, and that is also happening with this piece of
writing which I am reading here.
Now I am ready to do my breakfast, once having my breakfast coming over again to read more news.
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my website thus i came to “return the favor”.I am
trying to find things to improve my site!I suppose its ok to use a few
of your ideas!!
Aw, this was a really nice post. Spending some time and actual effort to generate a very good article… but what
can I say… I procrastinate a lot and don’t seem to get anything
done.
Wonderful beat ! I would like to apprentice even as you amend your
web site, how can i subscribe for a weblog site? The account aided me a acceptable
deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided vivid transparent concept
Truly no matter if someone doesn’t be aware of afterward its up to other users that
they will assist, so here it happens.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
I really like what you guys are up too. This
type of clever work and exposure! Keep up the awesome works guys
I’ve incorporated you guys to my own blogroll.
I really appreciate this post. I have been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thx again!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Greetings! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and say I really enjoy reading through your posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that deal with the same subjects? Many thanks!
The hard work you put into this post is as admirable as The commitment to high quality. It’s very attractive.
Hey, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Opera, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, terrific blog!
Compelling read with well-presented arguments. I almost felt persuaded. Almost.
If you wish for to get a good deal from this paragraph then you have to apply such methods to your won website.
Amoxicilina Amoxi Antibiotic By Money Order Store
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Looking forward to reading more. Great article.Really thank you! Cool.
Major thanks for the blog post.Really looking forward to read more.
I like what you guys are up too. This sort of clever work and reporting! Keep up the good works guys I’ve added you guys to blogroll.
I really enjoy the article.Thanks Again. Really Cool.
I loved your blog.Really looking forward to read more. Fantastic.
A round of applause for your blog post.Much thanks again. Keep writing.
A big thank you for your post.Really looking forward to read more. Awesome.
Thanks again for the article post. Really Great.
A big thank you for your article post.Much thanks again.
Enjoyed every bit of your article. Really Cool.
Thanks-a-mundo for the article.Much thanks again. Great.
I don’t really like livejournal or xanga. I already have both of those. I was going to try deadjournal because I read on here that it was really good, but I don’t want to have to pay for it and you have to have an invite code to get in free. Does anybody have an invite code they could give me, or a suggestion on another free blogging website I could try? Any information would be helpful..
It’s actually a great and useful piece of information. I am glad that you shared this helpful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
I really like and appreciate your article post.Really thank you! Cool.
I love to write. I mean, I really love to write. It’s probably the only passion I have stronger than love. But I need to know what college to go to.. . What college should I go to for Creative Writing?.
A big thank you for your blog article.Much thanks again. Really Cool.
I appreciate you sharing this blog post.Much thanks again. Fantastic.
Major thanks for the blog article.Much thanks again. Cool.
Hey, thanks for the article.Thanks Again. Much obliged.
Muchos Gracias for your article.Really thank you! Cool.
Looking forward to reading more. Great article.Really thank you!
Thanks-a-mundo for the article post. Fantastic.
Great, thanks for sharing this blog.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
Fantastic article post.Much thanks again. Cool.
Hey, thanks for the article post. Much obliged.
Say, you got a nice article.Thanks Again. Keep writing.
I loved your blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
wow, awesome article.Much thanks again. Really Great.
I truly appreciate this blog post.Really looking forward to read more. Will read on…
I am so grateful for your blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
I really liked your post.Really thank you! Fantastic.
Great forum posts. Many thanks!how to write a proper essay thesis writing services professional dissertation writing services
Muchos Gracias for your blog article.Really thank you! Great.
A round of applause for your blog article.Thanks Again. Awesome.
wow, awesome blog post.Really looking forward to read more. Really Great.
I truly appreciate this article.Thanks Again. Great.
Thanks for the article.Thanks Again. Want more.
Great, thanks for sharing this article.Thanks Again. Much obliged.
Fantastic article.Thanks Again. Keep writing.
Thanks so much for the blog.Really thank you! Great.
Thanks again for the blog post.Really looking forward to read more. Really Great.
Great, thanks for sharing this post.Really thank you!
I really like and appreciate your blog.Thanks Again. Much obliged.
foods not to take with azithromycin – azithromycin over the counter for humans zithromax dosing pediatric
Say, you got a nice article post.Really thank you! Will read on…
Hi there! I know this is kinda off topic but I’d
figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest writing a blog post
or vice-versa? My site discusses a lot of the same subjects as yours and I feel we could greatly benefit from each
other. If you happen to be interested feel free to send me an e-mail.
I look forward to hearing from you! Awesome blog by the way!
This post was a breath of fresh air, like a surprise message that brightens The day. Thank you for the lift.
I learned so much from this post. The ability to break down hard to understand ideas is something I really admire.
I’m extremely impressed along with your writing abilities
and also with the format on your weblog. Is this a paid subject or did you modify it yourself?
Anyway stay up the nice high quality writing, it is rare to look a
great blog like this one nowadays..
An intriguing discussion is worth comment. I do believe
that you ought to write more about this subject, it might not be a taboo subject but generally people don’t
speak about these topics. To the next! Many thanks!!
A big thank you for your blog.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
A round of applause for your article post.Really looking forward to read more. Really Great.
Greetings! I’ve been reading your blog for some time now and finally got the courage togo ahead and give you a shout out from New Caney Tx!Just wanted to tell you keep up the good job!
It’s really a nice and helpful piece of info. I am happy that you shared
this useful info with us. Please keep us informed like this.
Thank you for sharing.
Thanks again for the blog post.Thanks Again. Awesome.
I cannot thank you enough for the blog article.Thanks Again. Keep writing.
wow, awesome article.Really looking forward to read more.
Thanks again for the article post.Much thanks again. Cool.
wow, awesome post.Much thanks again. Awesome.
Hey, thanks for the blog.Really looking forward to read more. Fantastic.
Hello, Neat post. There’s an issue along with your web
site in internet explorer, might check this? IE nonetheless
is the market leader and a huge part of other people will miss
your great writing because of this problem.
Great, thanks for sharing this blog post.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
Very good post.Thanks Again. Cool.
Very informative article. Awesome.
Im thankful for the article.Really looking forward to read more. Really Cool.
I appreciate you sharing this blog.Really looking forward to read more.
Appreciating the time and effort you put into your site and detailed information you provide.
It’s nice to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the
same out of date rehashed information. Great read!
I’ve saved your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my
Google account.
These are really wonderful ideas in on the topic of blogging.
You have touched some good factors here. Any way keep
up wrinting.
wow, awesome article post.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
Really informative article.Much thanks again.
Very informative post. Great.
Hi to every , because I am actually keen of reading this
blog’s post to be updated daily. It includes fastidious stuff.
Fantastic article post.Really looking forward to read more. Fantastic.
Thank you for your blog article.Really looking forward to read more.
wow, awesome blog.Much thanks again. Cool.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
This is one awesome post.Much thanks again. Fantastic.
Looking forward to reading more. Great article.Thanks Again. Really Cool.
This blog was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something
which helped me. Thanks a lot!
Very good article. Really Cool.
Im obliged for the blog.Thanks Again. Will read on…
I am so grateful for your article.Really thank you! Much obliged.
wonderful issues altogether, you just received a logo new reader.
What would you recommend about your put up that you simply made some days in the past?
Any sure?
Great article post.Thanks Again. Really Great.
I’m extremely pleased to find this great site.
I need to to thank you for your time for this fantastic read!!
I definitely loved every bit of it and I have you bookmarked to see new things on your site.
I am not sure the place you are getting your info, but good
topic. I must spend some time finding out much more or figuring out more.
Thanks for magnificent information I was searching for this information for my mission.
I am in fact thankful to the holder of this site who has
shared this enormous piece of writing at here.
Very informative article.Thanks Again. Fantastic.
Hello there! I know this is kinda off topic nevertheless I’d figured I’d ask.
Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest writing a blog
article or vice-versa? My site covers a lot of the
same topics as yours and I think we could greatly benefit
from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free to send me an email.
I look forward to hearing from you! Wonderful
blog by the way!
I’m extremely inspired together with your writing abilities and also with the
structure for your blog. Is that this a paid theme
or did you customize it your self? Anyway stay up
the nice high quality writing, it is uncommon to
look a great blog like this one nowadays..
Thanks for sharing, this is a fantastic article.Thanks Again. Keep writing.
Excellent article. I definitely love this site.
Stick with it!
Thanks for sharing your info. I truly appreciate your efforts and
I will be waiting for your further write ups thank you once again.
I really like it when individuals come together and share thoughts.
Great website, keep it up!
Awesome issues here. I am very glad to look your post.
Thank you so much and I am having a look forward to touch
you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?
If you would like to increase your familiarity
just keep visiting this website and be updated with the latest news update
posted here.
Aw, this was an exceptionally nice post. Taking a
few minutes and actual effort to generate a good article… but what can I say… I put things
off a lot and never manage to get anything
done.
I always used to study article in news papers but now as
I am a user of web therefore from now I am using net for articles or reviews,
thanks to web.
Really appreciate you sharing this article.Really looking forward to read more. Really Cool.
It’s the best time to make a few plans for the longer term and it
is time to be happy. I’ve read this put up and if I may just I desire to suggest you some attention-grabbing things or advice.
Perhaps you could write next articles regarding this article.
I wish to read more things about it!
I don’t even understand how I stopped up here, but I assumed this post was great.
I do not recognise who you might be but certainly you are going to a famous blogger if
you aren’t already. Cheers!
You’re so cool! I do not believe I’ve read through anything like that before.
So great to discover another person with a few
genuine thoughts on this subject matter. Really..
thank you for starting this up. This web site is one thing
that’s needed on the web, someone with some originality!
Very informative blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
Say, you got a nice blog post.Much thanks again. Cool.
Thank you ever so for you blog post. Fantastic.
Looking forward to reading more. Great blog article.Really thank you! Cool.
Thanks a lot for the post.Really thank you! Really Cool.
Im obliged for the article.Really looking forward to read more.
Fantastic article.Really looking forward to read more. Fantastic.
Really enjoyed this blog post.Thanks Again. Much obliged.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Really informative blog.Much thanks again. Will read on…
Very good article post. Will read on…
Very good blog.Really looking forward to read more. Keep writing.
I cannot thank you enough for the blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
Asking questions are really nice thing if you are
not understanding something totally, however this piece of writing offers nice understanding
yet.
This is one awesome blog post.Really looking forward to read more. Will read on…