Introduction Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis , of which the seasonal type is called hay fever. This is an allergic reaction to tiny particles in the air called allergens. When you breathe in allergens through your nose or mouth, than your body reacts by releasing a natural chemical called histamine. Several indoor and outdoor allergens cause hay fever.
An allergy happens when the immune system mistakes a harmless substance for a harmful one, and the body releases chemicals to fight it.
Causes Allergic Rhinitis

Two types of cause
- Pollen related
- trees pollen
- weeds pollen
- Grass pollen
- Genetic factors
- If a close family member has hay fever or another allergy, the risk is higher
- Dust mites that live in carpets, drapes, bedding and furniture
- Pet dander (tiny flakes of dead skin)
- Cockroaches, including their saliva and waste.
- Mold spores.
- Food allergies can also cause inflammation in the nose and throat
Signs and Symptoms Allergic Rhinitis
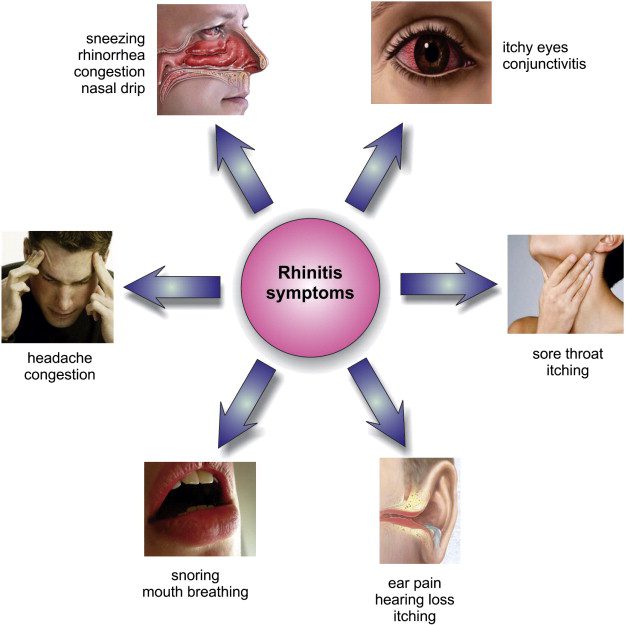
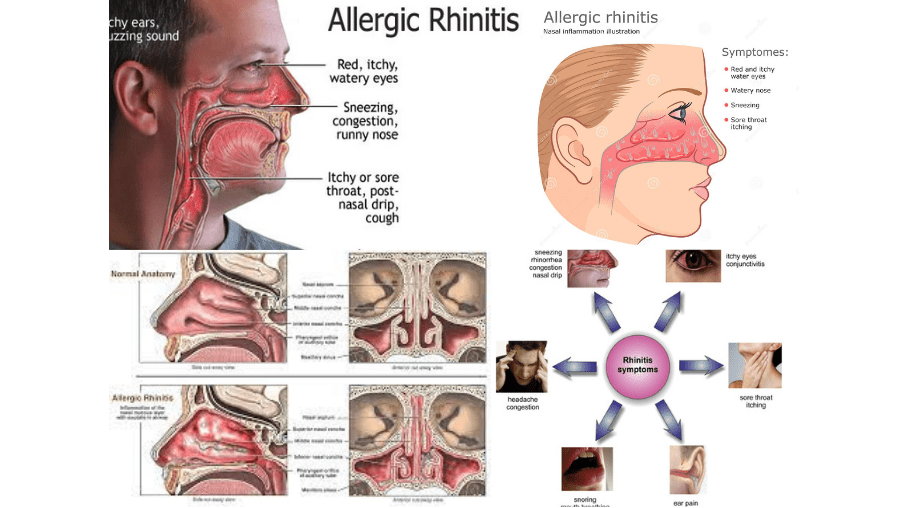
Common symptoms include:
- Rhinorrhea (excess nasal secretion)
- Itching
- Sneezing fits
- Nasal congestion and obstruction
- Conjunctival swelling and erythema
- Eyelid swelling with Dennie–Morgan folds
- Lower eyelid venous stasis
- Swollen nasal turbinate
- Middle ear effusion
Severe symptoms may include:
- Headaches
- Sinus pain
- Dark circles under the eyes
- Trouble breathing
- Fatigue and malaise
Classification
- Seasonal allergic rhinitis (hay fever)
- Perennial allergic rhinitis (non seasonal allergic rhinitis; atopic rhinitis)
Risk factor
Few factors increase the risk of hay fever or allergic rhinitis
- Genetic factors
- Other allergies or asthma
- Gender and age
- Birth date ( People born during the high pollen season have a slightly higher risk of developing allergic rhinitis )
- Second-hand smoke
Diagnosis
Allergy testing may reveal the specific allergens to which an individual is sensitive. But also include some test below
- Skin test
- Immunoglobulin E (IgE) test
- Skin prick test
- The RAST blood test
If a person has negative skin-prick, intradermal and blood tests for allergies. They may still have allergic rhinitis, from a local allergy in the nose. This is called local allergic rhinitis. Specialized testing is necessary to diagnose local allergic rhinitis.
Learn more about diseases
Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis or Hay fever

Several allergy medications can improve symptoms and help you live with hay fever. These treatments come in many forms, including some home treatment and some medicational treatment such as liquids, pills, eye drops, nasal sprays and injections.
Talk to your health provider before taking any medication, especially if you’re pregnant or have other health concerns. Your health provider may suggest two types treatment solution :
Home treatment
- Home treatment: people who experience hay fever may find some strategies useful for minimizing the impact. Here are some tips:
- Keep windows and doors shut when the pollen count is high.
- Be aware of the pollen count during susceptible months. Information is available through the internet and other media. Pollen count tends to be higher on humid and windy non-rainy days and during the early evening.
- Shower and change your clothes after coming indoors, when pollen counts are high.
- Regularly splash the eyes with cool water, to sooth them and clear them of pollen.
- Avoid mowing the lawn during susceptible months, choose low-pollen days for gardening, and keep away from grassy areas when pollen counts are high.
- Do not have flowers inside your home.
- Have your car fitted with a pollen filter, and drive with the windows closed at high-count times.
- Wear a hat to prevent pollen from collecting in the hair and then sprinkling down onto the eyes and face.
- Use wrap-around glasses to protect the eyes from pollen.
- Use “mite-proof” bedding.
- Use a dehumidifier to prevent mold.
- Keep all surfaces, floors, and carpets as dust free as possible.
- Choose a vacuum cleaner with a good filter.
- Wash pets when they come indoors on a high pollen count day, or smooth their fur down with a damp cloth.
- Keep away from cigarette smoke, and quit, if you are a smoker.
- Ask a physician for a plan, if you know your susceptible time is just around the corner.
- Smear Vaseline around the inside edges of your nostrils, as it helps stop pollen from getting through.
Medications treatment
- Medications treatment: The goal of rhinitis treatment is to prevent or reduce the symptoms caused by the inflammation of affected tissues. Measures that are effective include avoiding the allergen. Here are some may also choices your health provider. Such as-
- Antihistamines: They includes
- Loratadine
- Cetirizine
- Fexofenadine
- Levocetirizine
- Nasal corticosteroids: They includes
- fluticasone(Flonase)
- fluticasone (Veramyst)
- mometasone (Nasonex)
- beclomethasone (Beconase)
- Leukotriene inhibitors: Such as
- Montelukast
- Oral corticosteroids: Such as
- prednisolone
- Immunotherapy: This treatment works by helping your body learn to tolerate allergens. Your health provider gives you a series of injections (allergy shots) with a small amount of the allergen. Every time you get a shot, your provider increases the amount of the allergen. Over time, your immune system develops immunity to the allergen and stops launching a reaction to it. Your health provider might recommend immunotherapy in the form of a pill that you place under your tongue.
- Alternative therapies: Alternative therapies that claim to treat hay fever include acupuncture, but study results have not confirmed significant improvements. No herbal remedies are recommended.
- During pregnancy, it is important to speak to a doctor before taking any medication, to prevent potential adverse effects on fetal development.
- Antihistamines: They includes
Complications of Hay fever
Sad to say, allergic rhinitis itself can’t be Prevention. Treatment and management are only keys to achieving a good quality of life with allergies. Some complications that can arise from hay fever include:
- Development of asthma symptoms
- Sinusitis or persistent sinus infections
- Absences from school or work because of reduced potency.
- Incapacity to sleep from symptoms keeping you up at night
- continual ear infections
problem can also arise from antihistamine side effects. As usual, drowsiness can happen. Another side effects include headache, anxiety, and insomnia. IN exceptional cases, antihistamines can causes of gastrointestinal, urinary, and circulatory effects.
Prevention Of Allergic rhinitis or hay fever
The greatest way to prevent allergic symptoms is to manage your allergies. Before your body has a chance to respond to substances negatively. Consider the following protective measures for the particular allergens you’re sensitive to:
- Pollen
- Dust mites
- Pet dander
Prevention often focuses on avoiding specific allergens that cause an particular’s symptoms. These methods include not having pets, carpets or upholstered furniture in the home and protecting the home dry. Specific anti-allergy attachment covers on household items like pillows and mattresses have also proven to be effective in preventing dust mite allergies.
Tips to prevent allergies
- Keep your windows and doors shut as usually as possible during allergy season
- Keep your mouth and nose covered while executing yard work
- Remove carpeting from your bedroom if you’re worried about dust mites
- Bathe your dog at least twice per week to minimize scurf
- Avoid exercising out-of-doors early in the morning
- Stay indoors when pollen counts are raised
- Try not to rake leaves or cutting the lawn
Learn more about this disease




I simply could not depart your site prior to suggesting that I actually loved the usual info a person provide on your visitors? Is gonna be again steadily to check up on new posts
Hi, Neat post. There’s a problem along with your website in internet explorer, may check this?K IE nonetheless is the market chief and a good section of other people will leave out your wonderful writing due to this problem.
Simply wanna input on few general things, The website layout is perfect, the articles is real excellent. “Some for renown, on scraps of learning dote, And think they grow immortal as they quote.” by Edward Young.
I’ve been browsing online more than three hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It is pretty worth enough for me. In my view, if all webmasters and bloggers made good content as you did, the net will be much more useful than ever before.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for any other informative blog. Where else could I am getting that type of information written in such an ideal method? I’ve a challenge that I am just now working on, and I have been at the glance out for such info.
Great ?V I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs as well as related info ended up being truly simple to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Quite unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Nice task..
I do agree with all of the ideas you have presented in your post. They are very convincing and will definitely work. Still, the posts are too short for starters. Could you please extend them a little from next time? Thanks for the post.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
The article was a joy to read, and The enthusiasm is as infectious as The charm.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Well I sincerely liked reading it. This post procured by you is very practical for accurate planning.
Great blog here! Also your web site loads up very fast! What web host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my site loaded up as fast as yours lol
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you ever so for you article.Thanks Again. Fantastic.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
fantástico este conteúdo. Gostei bastante. Aproveitem e vejam este site. informações, novidades e muito mais. Não deixem de acessar para aprender mais. Obrigado a todos e até mais. 🙂
There are some fascinating closing dates in this article but I don’t know if I see all of them heart to heart. There’s some validity but I will take maintain opinion until I look into it further. Good article , thanks and we want extra! Added to FeedBurner as effectively
Bookmarking this for future reference, but also because The advice is as invaluable as The attention.
I always learn something new from The posts. Thank you for the education!
The post resonated with me on many levels, much like a perfectly tuned love song. Thanks for the harmony.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.