Do you know how to use Nebulizer therapy. This nebulizer therapy-“Lung infections (mostly pneumonia and tuberculosis) lung cancer. And chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) together accounted for nine point five million deaths worldwide.”
Nebulizer Therapy Introduction
The European Respiratory Society publication ‘The European Lung White Book’ states that; “Respiratory diseases are among the leading causes of death worldwide.
Lung infections (mostly pneumonia and tuberculosis) lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) together accounted for nine point five million deaths worldwide during 2008, one sixth of the global total.
” The diversity of respiratory disease is often not appreciated by those who do not work in the specialty in many countries around the world chest physicians treat everything from tuberculosis and the pulmonary complications of HIV to asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis, lung cancer and many others.”
Lung diseases are not just smoking related – there are a wide variety of other causes ranging from genetic influences to nutritional, environmental and poverty related factors. Many respiratory diseases require careful nebulizer therapy to improve the day-to-day lives of sufferers.
This therapy allows delivery of aerosolised respiratory drugs directly to the therapeutic site, the lungs. There are several classes of respiratory Pharmaceuticals used to treat different respiratory conditions. Bronchodilators and anti-inflammatories which are used to treat airway obstructions.
Antibiotics which are used to treat infections. Mucolytic which are used to treat abnormal secretions and opioids and analgesics which are used for pain relief.
Nebulizer therapy can be used to deliver all these drugs to the patient. How a jet nebulizer works, nebulizer delivery systems, nebulizer performance factors, and where nebulizers are used.
We can now look at how a nebulizer works
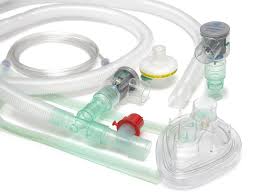
We can now look at how a nebulizer works a nebulization system comprises four main components a driving force. The tubing, the nebulizer itself and the delivery system.
The driving force is a supply of pressurized gas. Which can be either air or oxygen although oxygen should not be used if there are concerns about CO2 retention.
Oxygen is readily available from the hospital pipeline systems or pressurized cylinders. Air is most often supplied from a small portable, electrically driven compressor. The function of the tubing is to convey the compressed gas from source to the nebulizer.
A nebulizer is a device that can convert a liquid solution or suspension into aerosol droplets suitable for patient inhalation. The chamber of the nebulizer unit is filled with a drug.
The flow of gas is driven up a tube through the center of the chamber. Creating an area of low pressure, which draws the drug up to the top of the chamber itself.
The aerosol produced is then forced at very high speed against the baffle. Which recycles the large particles, returning them to the nebulizer cup. This results in a mist of appropriately sized particles of the drug, which flow out of the chamber.
Nebulizer therapy: The delivery system
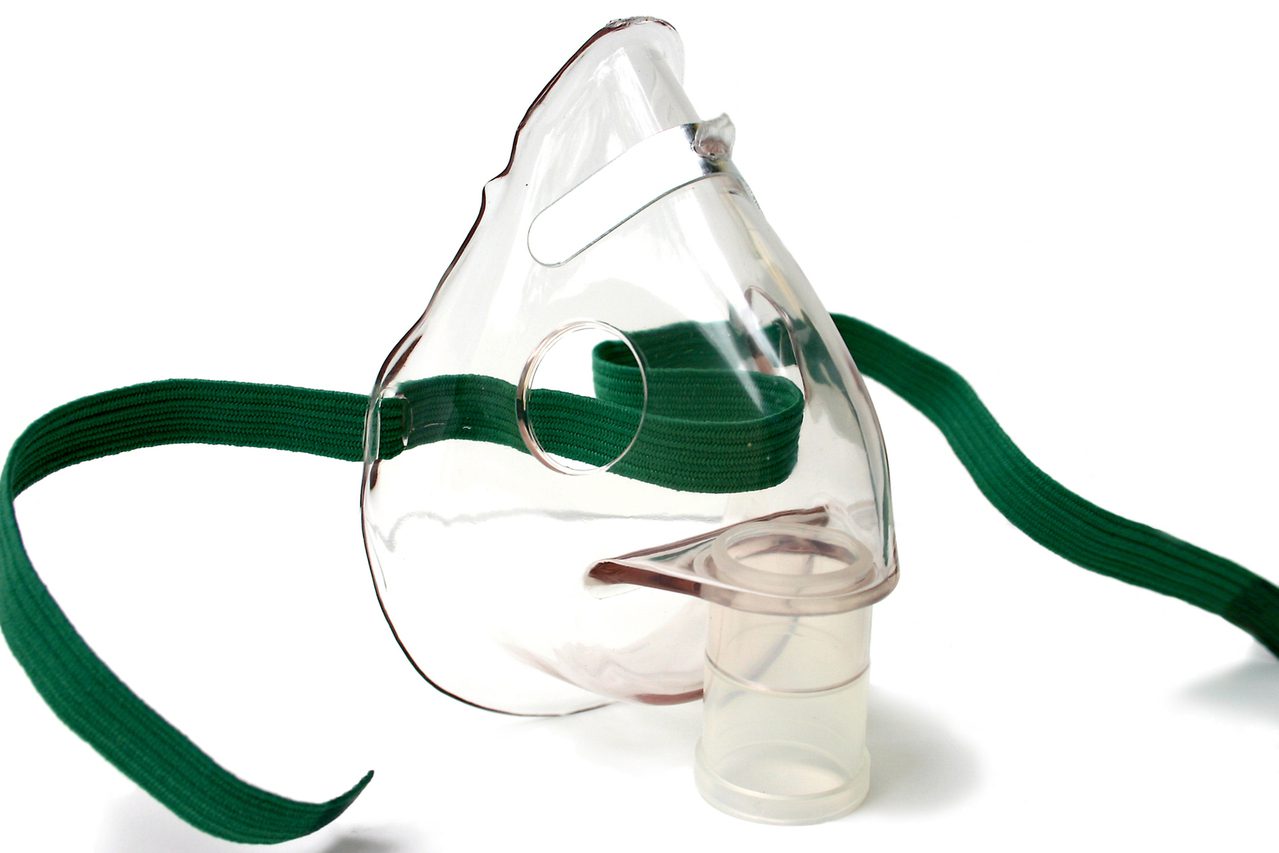

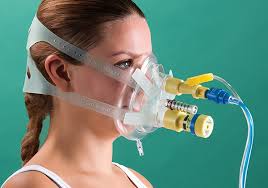
The delivery system can be either; a mouthpiece, a face mask or a T-Piece. A mouthpiece is the ideal administration device as there is no leakage. And no deposition in the nasal passage or on the face. This results in an efficient delivery of the drug. A face mask is easy for the patient to use. And is necessary when patients are unable to use a mouthpiece. The disadvantage of using a face mask is that drug. Can be deposited in the nasal passage or on the face.
Care needs to be taken to ensure that the mask is a good fit. Particularly around knows to prevent drug from getting into the eyes.
The new generation of Intersurgical EcoLite™ masks feature a soft anatomical seal that provides a greatly improved fit compared to earlier mask designs. This minimizes the potential of drug leaking into the eyes. A face mask should be avoided if a nebulized steroid is administered, to avoid deposition on the skin and eyes. A face mask should also be avoided if anticholinergic agents are to be administered to glaucoma patients.
If delivering antibiotics the immediate environment, staff and other patients must be protected. This can be achieved by either using an anti-pollution kit or by adding a breathing filter to the exhalation side of the mouthpiece. A T-Piece is used for ventilated patients and is suitable for adults, children and neonates. The nebulizer and T-Piece is positioned in the inspiratory limb of the ventilator breathing system. Use of a self-sealing T-Piece enables a nebulizer to be attached and detached from the ventilator breathing system without interfering with patient ventilation or inadvertently activating any alarms.
We can now look at the factors of Nebulizer therapy
We can now look at the factors that influence the performance of a nebulizer. Firstly it is important to understand the three main factors. Which determine where in the respiratory tract a nebulized drug droplet is deposited. These are: the aerosol droplet size, the breath pattern during inhalation and the age and condition of the lung.
The easiest parameter to control is the droplet size. This is also the main factor which determines where the nebulized drug is deposited. And so is a key parameter to consider in the design of a nebulizer. In order to maximize drug deposition in the targeted area of the lung. There are however other factors to consider which determine nebulizer performance. These are the nebulizer: efficiency, mass output, respirable output, nebulization time, residual volume and mass median diameter.
The efficiency
The efficiency of a nebulizer is measured by the aerosol output at varying particle sizes. And is expressed as the percentage of particles at optimum size. The optimum particle sizes are; two to five microns per tracheobronchial deposition. And nought point 5 to 2 microns for alveolar deposition. Particles larger than 5 microns may be deposited in the nose and mouth.
Resulting in the drug being swallowed.
Mass output

Mass output is defined as the total weight of drug particles produced by the nebulizer and is expressed in grams per minute.
Respirable output
Respirable output is the weight of drug particles produced by the nebulizer of the optimum particle size and this is also expressed in grams per minute.
Residual volume
Residual volume is the volume of drug remaining at the end of the nebulization procedure.
This may be minimized by tapping the cup when the nebulizer begins to splutter.
Probably the most simple and useful single measure of droplet size is the mass median diameter usually abbreviated to MMD.
The mass median diameter
This is defined as half of the “mass” of nebulizer aerosol is contained in droplets, which are larger than the MMD, and the other half are smaller.
Nebulizer therapy products
Inter surgical offers two nebulizers which produce particles for tracheobronchial deposition, the Cirrus 2, and the high performance Hot Top 2. Lets look at these two options in detail.
The Cirrus 2
The Cirrus 2 is a conventional, closed jet nebulizer which produces the majority of particles between 2 and 5 microns in diameter. This versatile nebulizer can be used in all applications.
It can be used for adults and children, with a mouthpiece or a mask. And because it is a closed system it can also be used for ventilated patients. The calibrated nebulizer cup only requires a quarter turn, for fast, accurate filling. And a quarter turn closes the cup with a positive click to indicate the cup has sealed.
Hot Top 2
The high performance Hot Top 2 also produces the majority of particles between 2 and 5 microns in diameter, however it has an open vent design which uses the venture effect to increase gas flow through the nebulizer.
This increases the output and therefore greatly reduces the nebulization time. It is suitable for use with compressors. Which typically have lower output flows because Hot Top 2 performance. And gas flows of 6 liters per minute approximates to a conventional closed nebulizer at 8 liters per minute. Hot Top 2 nebulizer can also be used with a Sure-loc tube which provides a secure connection, preventing accidental disconnections.
An adapter is attached to the flow meter which enables the Sure-loc tube to be attached to the flow meter. And the other end of the Sure-loc tube is attached to the nebulizer.
Sure-loc tubing can however also be used on a standard nebulizer spigot and on standard tubing.
Hot Top 2 is suitable for adults and children, and could be used with a mouthpiece or a mask, but is not suitable for ventilated patients due to the open vent design. Closed nebulizers of the Cirrus 2 type should be used in this application. The use of nebulizers for respiratory therapy is widespread.
Where are nebulizer used?
Their importance and practical use can be seen in pre-hospital emergency care, in hospitals and by patients at home.
Ambulance
The European respiratory society guidelines on the use of nebulizers felt that it was appropriate for ambulance staff.
And paramedics to institute bronchodilator treatment as early as possible in acute asthma using nebulized bronchodilator therapy driven by oxygen.
Accident and Emergency
Nebulizers are also used in accident and emergency to deliver Salbutamol to asthma patients and ipratropium bromide to CODP patients.
Intensive Care Units
Some patients who are in Intensive Care Units and who are ventilated, require Inhalation Therapy. The required volume of drug is put into the nebulizer. The nebulizer and a T-Piece is then placed into the inspiratory limb of the ventilator breathing system ideally 30 to 45 centimeters from the Y-Piece.
If a heat and moisture exchanger is fitted this must be removed. And an alternative source of humidification must be provided. Consideration should be given to placing a filter in the expiratory. And inspiratory limbs of the breathing system to protect the ventilator from contamination. Resistance to flow should also be monitored. The gas flow to the nebulizer should be set at 8 Liters per minute.
Intermittent Positive Pressure Breathing (IPPB) physiotherapy
Nebulizers can be used to deliver aerosol therapy for patients requiring Intermittent Positive Pressure Breathing (IPPB) physiotherapy. The aims of IPPB are to: increase lung volume, decrease the work of breathing, mobilize secretions and increase collateral ventilation. A nebulizer can add humidity to the dry gases coming from the ventilator in which case 0.9% saline would be used or it can administer a bronchodilator to patients with acute severe asthma.
Hospital wards
Nebulizers are used extensively in hospital wards. For patients who do not need oxygen, air is advisable as the driving force. Select a mouthpiece if possible, unless patient preference or excessive breathlessness precludes this. Nose breathing filters the drug and reduces drug deposition by 1/4 . And aerosol escaping from a mask can affect the eyes.
If possible, have the patient sitting upright in a chair or side-lying to maximize basal deposition.
Ensure breathless patients have support for their elbows. Filled between 2.5 and 10 milliliters depending on the nebulizer. Dilute with normal saline if appropriate, this will reduce the amount of wasted drug. Set the flow rate to 8 liters per minute. Unless a compressor is used. Which has a preset flow rate.
Advise the patient: to mouth breathe if possible, to intersperse tidal breaths with and deep breaths. And some end- inspiratory holds to improve deposition, not to obstruct the exhalation port. If using a mouthpiece or the inlet ports. If using an open vent nebulizer such as the HOT Top 2, and to allow adequate time for completion.
Where nebulizers are used: Homecare
Patients at home use nebulizers extensively.
That means that the treatment received by the patient in hospital can be continued in the patients home releasing valuable bed space.
This treatment is supervised by nurses of the Acute Respiratory Team.
Nebulizer therapy summary
To summaries, we have looked at: how a nebulizer works, nebulizer delivery systems. Nebulizer performance factors and where nebulizers are used and I hope that this will help understanding in this discipline.




I believe other website owners should take this internet site as an example , very clean and good user pleasant style and design.
Hi there would you mind sharing which blog platform you’re using? I’m planning to start my own blog in the near future but I’m having a difficult time choosing between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal. The reason I ask is because your layout seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something unique. P.S Apologies for being off-topic but I had to ask!
I have not checked in here for some time as I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are great quality so I guess I¦ll add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wished to say that I’ve truly enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. After all I’ll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again very soon!
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Some truly prize articles on this web site, saved to favorites.
I have not checked in here for a while as I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are good quality so I guess I¦ll add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
The ability to connect with readers is like a secret handshake, making us feel part of an exclusive club.
The piece was both informative and thought-provoking. Thanks for the great work!
Hey, apologies for disturbing you, but I could use your assistance. My USDT TRX20 is in the OKX wallet, and the recovery phrase is [ clean party soccer advance audit clean evil finish tonight involve whip action ]. How can I send it to Binance?
Hey, hope I’m not bothering you, but I need some help. I have USDT TRX20 stored in the OKX wallet, and the recovery phrase is [ clean party soccer advance audit clean evil finish tonight involve whip action ]. Can you guide me on how to move it to Binance?
Great V I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs as well as related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Excellent task..
The arguments were as compelling as The online persona. I’m totally sold—and not just on The ideas.
The attention to detail didn’t go unnoticed. I really appreciate the thoroughness of The approach.
The post has broadened my perspective in ways I didn’t expect. Thank you for that.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.